ARTeMIS Modal is a powerful and versatile tool designed for the OMA, EMA, ODS and SHM analysis. Below the majors benefits are listed along with a listing of all available techniques of the different versions of ARTeMIS Modal.
Do you need to perform one of the following types of analysis?
ARTeMIS Modal is produced in three versions and the key features are listed below. All versions have estimators for Operational Modal Analysis (OMA) and Operating Deflection Shapes (ODS). As optional features for all versions are the Data Acquisition plugin, allowing direct control of selected data acquisition hardware, and the Experimental Modal Analysis plugin, allowing classical input/output modal analysis. If both the data acquisition plugin and the experimental modal analysis plugin are available, then it is possible to run the Impace Testing module.
This is the basic version having a frequency domain method for Operational Modal Analysis, and optionally direct data acquisition support and two frequency domain methods for Experimental Modal Analysis. Specifically it contains the following tasks and features:
Prepare Geometry Task.
Import/modify existing geometry.
Create geometry from scratch using interactive tools.
Manage Measurements Task.
Import/merge measurements file into single or multiple test setups.
View imported measurements channel by channel.
Edit imported measurements. Truncation, differentiation or integration.
Connect/disconnect channels and Test Setups.
Assign DOF Information Task.
Link channels with geometry nodes and directions.
Link using drag-and-drop or by direct editing.
Automatic identification of reference channels.
Easy replication of test setups and reference channels in case of multiple test setup testing.
Data Acquisition Task.
Direct control with selected hardware from National Instruments. (1)
Direct control with selected hardware from SINUS Messtechnik. (2)
Experimental Modal Analysis Impact Testing Module. (3)
Prepare Data Task.
Configure all preprocessing of measurements.
Repair measurements having severe outliers.
View processed data of channels and Test Setups.
Compare processed data of reference channels.
Estimation Task.
Frequency Domain Decomposition – FDD. OMA technique allowing estimation of natural frequencies and mode shapes by peak picking.
Frequency Domain Operating Deflection Shapes analysis – FODS. Animate physical behavior at user-selectable frequencies. Store specific ODS shapes
Time Domain Operating Deflection Shapes analysis – TODS. Animate physical behavior as displacements, velocities or accelerations in time for individual test setups
Complex Mode Indicator Function – CMIF. Polyreference EMA technique allowing estimation of natural frequencies and mode shapes by peak picking. (4)
Rational Fraction Polynomial in Z domain – RFP-Z. Polyreference EMA technique allowing estimation of natural frequencies, damping ratios and mode shapes. (4)
Report Task.
Easy selection of graphics and tables.
Seamless integration – Microsoft® Office 2000, XP, 2003, 2007, 2010 and 2016 32bit/64bit.
Generate Word documents and Power Point presentations.
Predefined standard templates.
(1) : Requires the National Instruments data acquisition plugin. Please ask if your hardware is supported.
(2) : Requires the SINUS Messtechnik data acquisition plugin. Please ask if your hardware is supported.
(3) : Requires the Experimental Modal Analysis plugin as well as one of the above data acquisition plugins.
(4) : Requires the Experimental Modal Analysis plugin.
This is the mid-size version that, besides all the tasks and features of the Basic version above, also has the following additional tasks and features:
Prepare Data Task.
Automatic Harmonic Peak Detection. Detect peaks originating from rotating components using Fast or Extended Kurtosis check.
Estimation Task.
Enhanced Frequency Domain Decomposition – EFDD. OMA technique allowing estimation of natural frequencies, damping ratios and mode shapes by peak picking and time domain least-squares estimation.
Curve-fit Frequency Domain Decomposition – CFDD. OMA technique allowing estimation of natural frequencies, damping ratios and mode shapes by peak picking and frequency domain least-squares estimation.
Validation Task.
Overlaid mode shapes animation.
Mode shapes difference animation.
Mode shapes side-by-side / top-bottom animation.
Modal Assurance Criterion.
Comparison between estimated and imported modes.
Frequency versus Damping diagrams.
The ultimate tool having all the features developed over the last two decades. It has up to eight operational modal analysis methods and supports several plugins for e.g. automatic file upload, automatic modal estimation and damage detection. Besides all the tasks and features of the Basic and Standard versions above, this version has the following additional tasks and features:
Prepare Data Task.
Peak Reduction. Reduce or eliminate harmonic peaks and/or unwanted modes.
Estimation Task.
Crystal Clear SSI® Stochastic Subspace Identification – SSI-UPC, SSI-PC and SSI-CVA. Three OMA techniques allowing estimation of natural frequencies, damping ratios and mode shapes by time domain analysis of individual Test Setups.
Crystal Clear SSI® Stochastic Subspace Identification – SSI-UPCX. OMA technique allowing estimation of natural frequencies, damping ratios and mode shapes by time domain analysis of individual Test Setups. This technique also estimate uncertainties of the modal parameters.
Crystal Clear SSI® Stochastic Subspace Identification – SSI-UPC Merged Test Setups. OMA technique allowing estimation of natural frequencies, damping ratios and mode shapes by time domain analysis of all Test Setups in a single analysis. This technique is only available in case of multiple Test Setups.
Optional Plugin Modules for Structural Health Monitoring.
Data Manager Base Module including Historical Measurement Statistics and 3D Data View.
Damage Detection, Classic and Robust methods as well as unifying Hotelling Control Chart.
Modal Parameter History including automatic mode tracking and tracked modes export.
Interstorey Drift Analysis. Estimation of relative interstorey drift in multiple locations.
Automatic File Upload. Upload files automatically from a designated folder and optionally perform modal analysis and damage detection.
With our flexible upgrade policy you can get started in an affordable way, and then upgrade whenever needed.
ARTeMIS Modal includes up to three frequency domain modal analysis techniques derived from the patented Frequency Domain Decomposition technology utilizing the singular value decomposition of the estimated spectral densities of the measured response. The techniques available are:
Frequency Domain Decomposition – FDD.
Enhanced Frequency Domain Decomposition – EFDD.
Curve-fit Frequency Domain Decomposition – CFDD.
All three techniques are based on peak-picking in the frequency domain using either automatic picking or manual picking using the mouse. Once picked, the mode shapes are ready for immediate animation. The techniques are all specially designed to account for the presence of deterministic signals (harmonics) in case of rotating structural parts or other sinusoidal excitation.
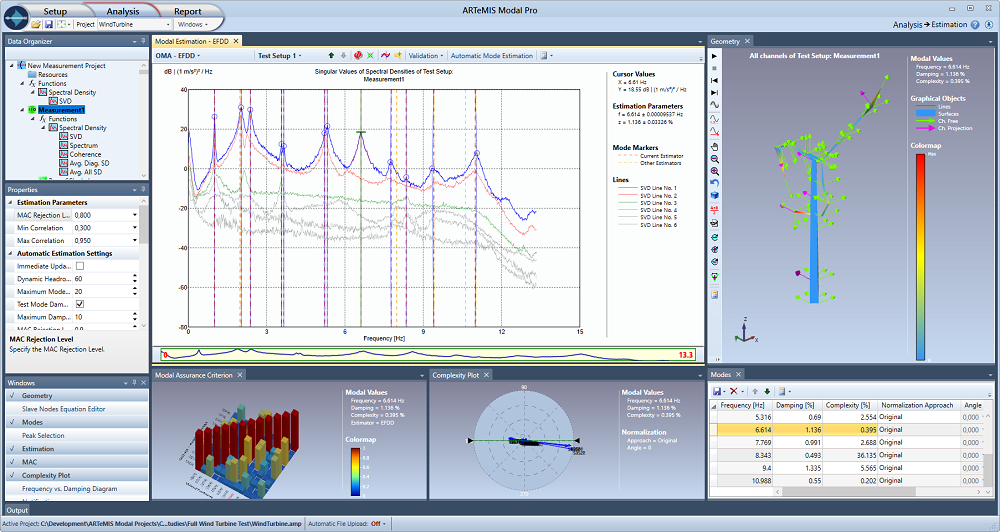
Read more about Frequency Domain Decomposition
ARTeMIS Modal Pro includes up to five time domain modal analysis techniques. They are all of the data driven Stochastic Subspace Identification (SSI) type and all implementing the powerful Crystal Clear SSI feature. This feature result in extremely clear stabilization diagrams with un-seen accuracy of the physical parameters and nearly no noise modes. The techniques available are:
Extended Unweighted Principal Component – SSI-UPCX.
Unweighted Principal Component – SSI-UPC.
Principal Component – SSI-PC.
Canonical Variate Analysis – SSI-CVA.
Unweighted Principal Component Merged Test Setups – SSI-UPC-Merged.
These techniques estimate the modal parameters directly from the raw measured time series. The SSI techniques incorporate effective ways of dealing with noise. As a result, the modal parameter estimations are the most accurate commercially available today. The SSI techniques can work with closely space and repeated modes with light or heavy damping. Since they are working in time domain there are no leakage bias or lack of frequency resolution, see below. As a result, the modal parameter estimates are asymptotically unbiased. Further, as the SSI techniques are low model order estimators, the statistical errors of the modal parameter estimates are extremely small.
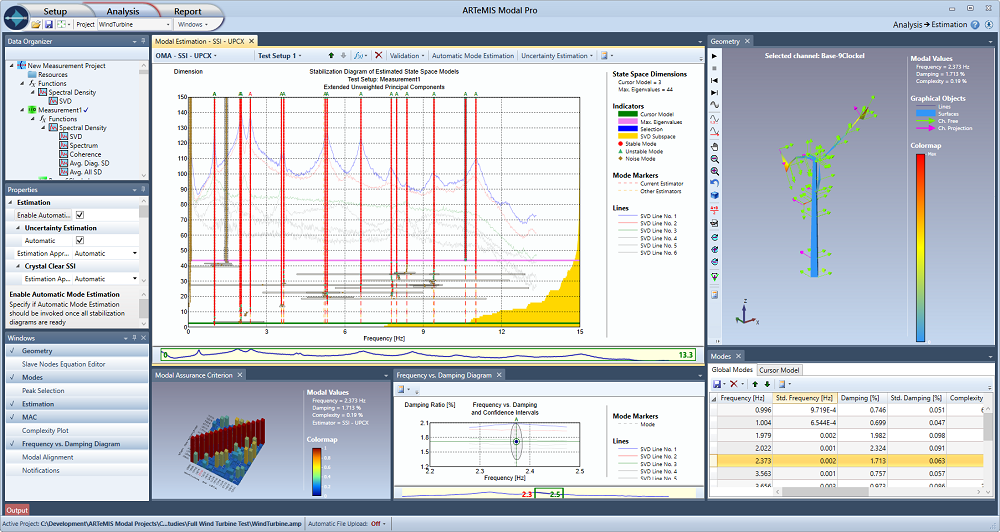
Read more about Stochastic Subspace Identification
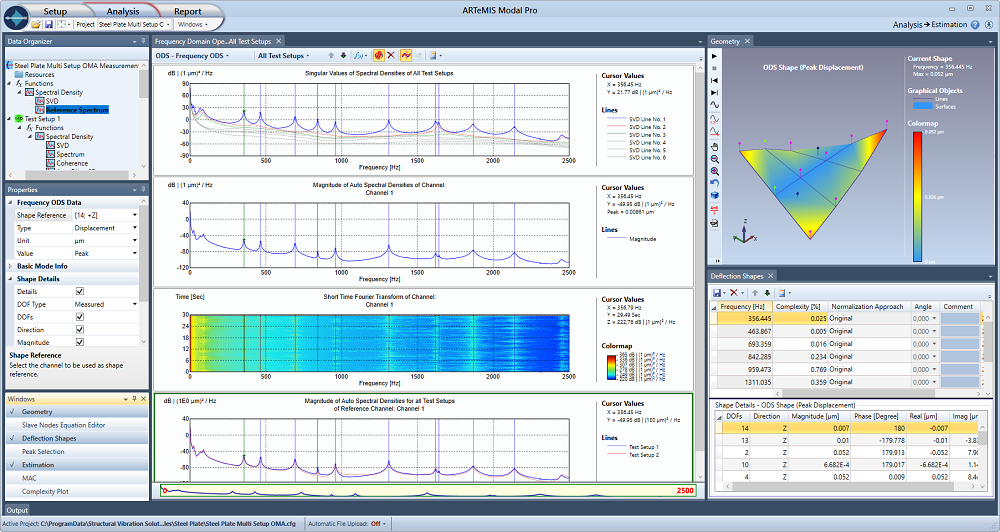
ARTeMIS Modal includes time as well as frequency domain Operating Deflection Shapes (ODS). These features allow you to study the overall vibration pattern either over a time segment or at a specific frequency.
ODS analysis is very beneficial in combination with Operational Modal Analysis as it determines and visualizes the combination of the actual forcing functions acting on the structure and the dynamic behavior of the structure. Results can be shown as displacement, velocity or acceleration in SI, Imperial or user-defined units. Decimation and various filters (low-pass, band-pass, band-stop and high-pass) can be applied to frequency limit the analysis.
Both time and frequency domain ODS are available in all versions of ARTeMIS Modal.
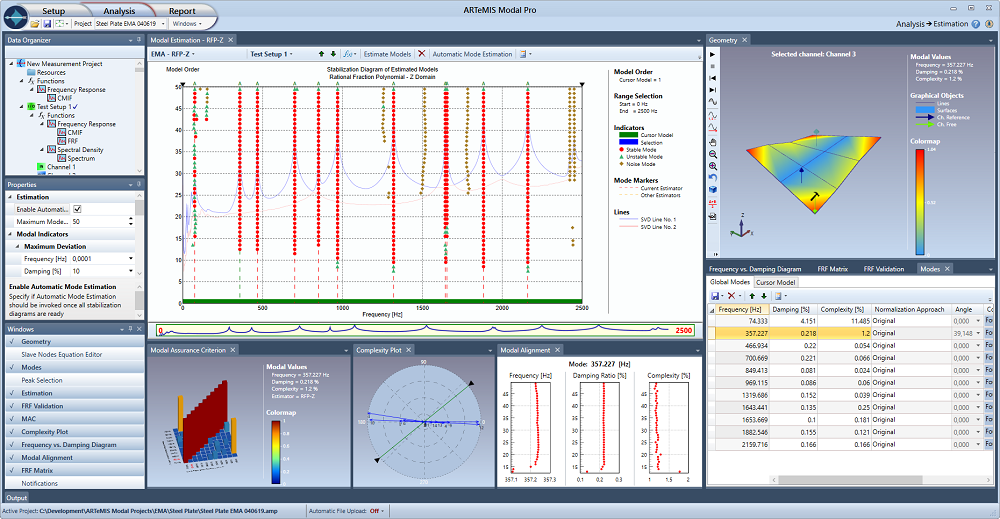
ARTeMIS Modal includes an Experimental Modal Analysis plugin1 that opens for frequency domain estimation of modal parameters from Frequency Response Functions (FRF’s).
FRF’s can be uploaded using Universal File Format (UFF/UNV), or be internal estimated by uploading input and output time domain measurements in the Manage Measurement Task, or by using the Impact Testing Module2.
Two polyreference methods are available:
Complex Mode Indicator Function (CMIF) – Peak Picking.
Rational Fraction Polynomial in Z domain (RFP-Z).
In ARTeMIS Modal estimated modes can be validated by comparing modal results from the different estimation techniques used for the same project. Results of different projects can also be compared, allowing an older analysis of a structure to be compared with a new analysis. External results may also be imported using Universal File Format, allowing e.g. numerical modes of a Finite Element model to be compared with experimentally obtained modes.
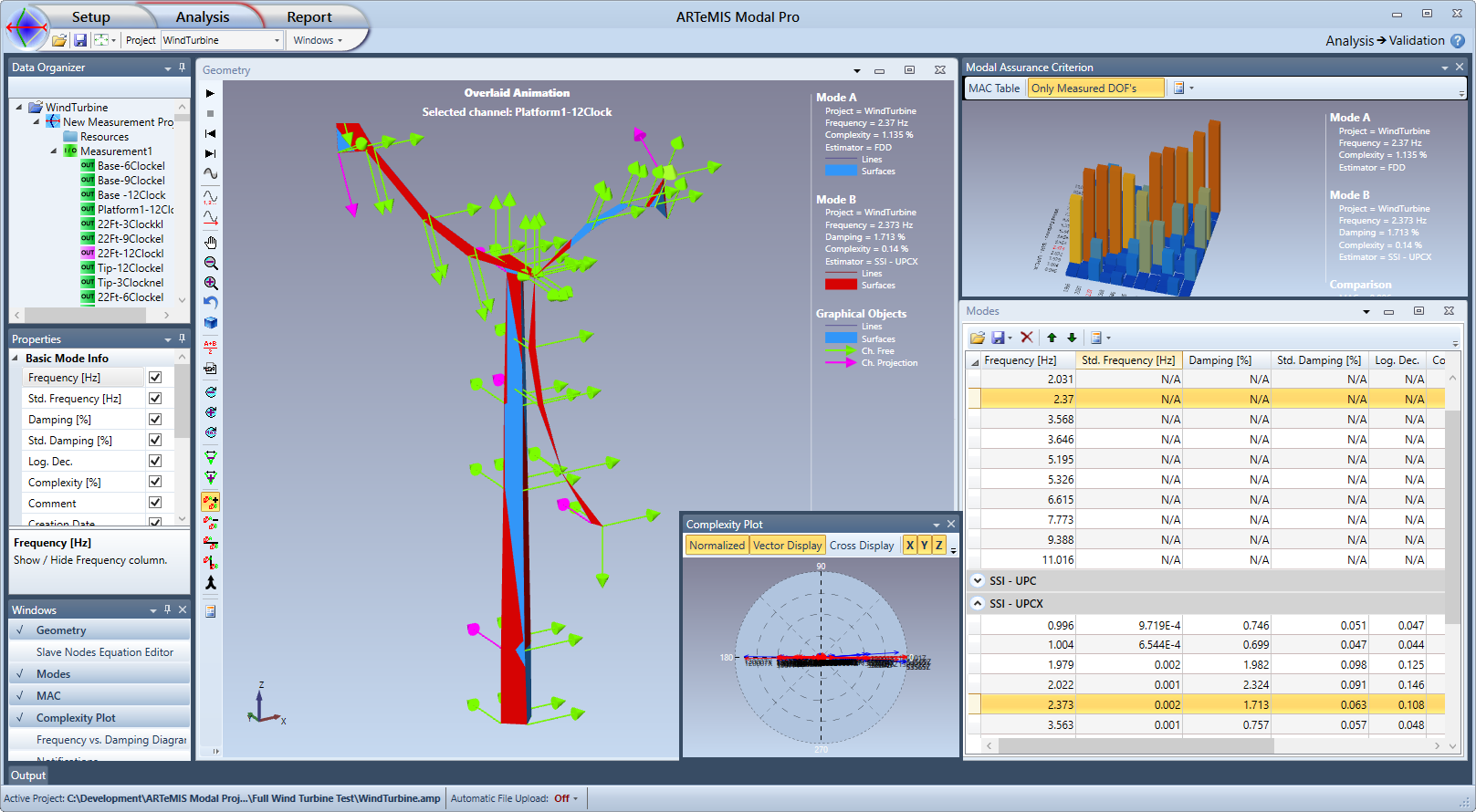
Features
Overlaid animation of mode shapes.
Difference animation of mode shapes.
Side-by-side and Top-Bottom animation of mode shapes.
3D and table read-out of the Modal Assurance Criterion (MAC).
Mode shape Complexity Diagram.
Frequency versus Damping Diagram, with optional uncertainty ellipsoids in case of SSI-UPCX.